Count duplications and losses in the presence of polyploidy
Below are the inputs, commands, and outputs to do an analysis with GRAMPA to count the number of duplications and losses in a set of gene trees in the presence of polyploidy. The inputs are based on simulated data. For more detailed info on the simulations check our paper.
The examples below call GRAMPA as grampa assuming it has been installed from bioconda. If you installed
from source, see usage details in the README.
Inputs
Suppose a hybridization event between the B and C lineages leading to the allopolyploid x,y,z clade. The MUL-tree representing this scenario is:
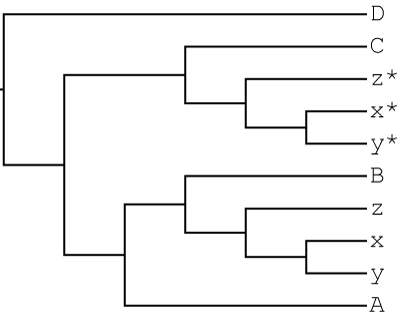
GRAMPA can accurately count duplications and losses with this MUL-tree as input.
- MUL-tree: mul_tree_74_3a.tre
- Gene trees from your set of species (in this case 1000 gene trees simulated with gain and loss) : gene_trees_3a.txt
GRAMPA command
With a known polyploidy scenario (MUL-tree), we can simply reconcile to that MUL-tree:
grampa -s mul_tree_74_3a.tre -g gene_trees_3a.txt -o ex3-output -f count-test --multreeThe --multree flag is required in this case to let GRAMPA know that the input species tree is a MUL-tree.
Outputs
The above command would create the directory ex3-output with five output files
- count-test-checknums.txt
- count-test-detailed.txt
- count-test-dup-counts.txt
- count-test.log
- count-test-scores.txt
Since we are trying to count duplications and losses, we are interested in the count-test-detailed.txt file. This file contains
reconciliation scores for each gene tree to the lowest scoring MUL-tree (in this case, the only MUL-tree). The contents of the file look something
like this:
mul.tree gene.tree dups losses total.score
1 1 5 2 7
1 2 8 4 12
1 3 3 0 3
1 4 1 4 5
Here you can see the exact number of duplications and losses for each gene tree when mapped to the lowest scoring MUL-tree, while properly
counting multiple copies of the polyploid species (x,y,z) as either paralogs or homoeologs. Additionally, you could add the
--maps flag to the command above to add another column to the detailed output file that shows the maps and
duplication nodes in each gene tree (see the README section --maps for more info).
Additionally, GRAMPA counts the total number of duplications across all gene trees for each node in the six lowest scoring trees. In this
example, we only searched one tree so it only provides the duplication counts for that tree. These counts can
be found in the count-test-dup-counts.txt file:
mul.tree node dups
1 x* 102
1 y* 88
1 z* 193
1 B 234
1 A 344
1 C 232
1 x+ 104
1 y+ 87
1 z+ 212
1 D 386
1 <1> 94
1 <2> 82
1 <3> 102
1 <4> 73
1 <5> 110
1 <6> 101
1 <7> 143
1 <8> 108
1 <9> 0